Exporting Mascot PSMs
Redundancy handling
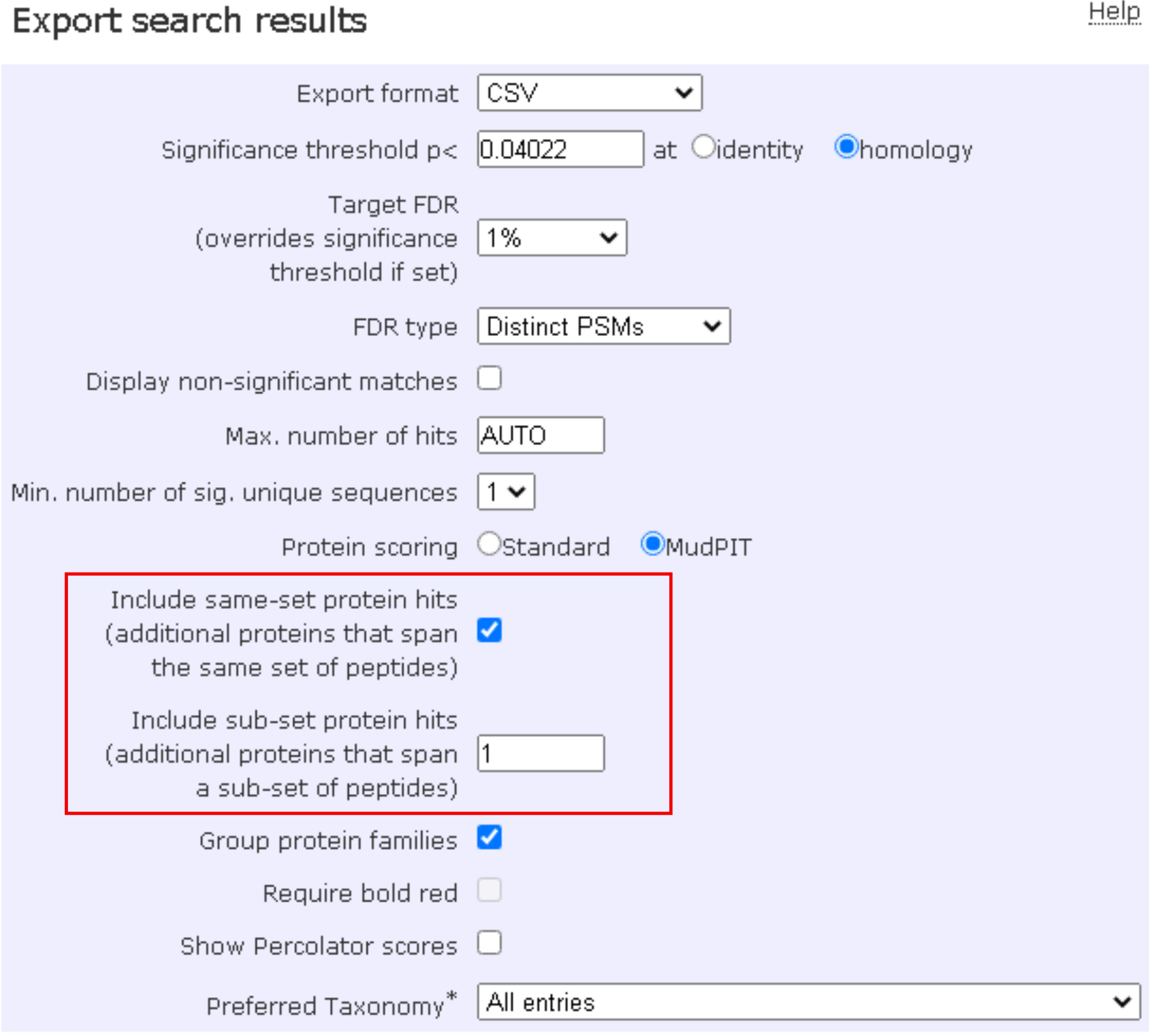
When exporting Mascot PSMs, one choice is to apply upfrontly the principle of parsimony by excluding both same-set and sub-set proteins (2011) whose presence may not be unambiguously determined. Alternatively, the redundancy might be at first permitted and handled later (see also Data preprocessing). The same-set and the sub-set proteins will be eventually removed from the compiled PSM reports.1 In spite, there is a subtle difference.
With the Include same-set protein hits being checked and the Include sub-set protein hits set to 1, proteoQ will further parse out (Occam’s) razor peptides that are shared among representative and same-set and/or sub-set proteins. The additional information, summarized under columns pep_razor_unique and pep_literal_unique in PSM outputs, would allow the probable exclusion of the razor peptides for more strict quantitation of proteins.
Additional fields
Mascot offers a handful of options for exporting PSMs. The flexibility might have been intended for balancing the performance between higher time efficiency and finer data granularity, by leaving the choices to users. When coupling to proteoQ, it is generally suitable to check as many items as desirable, with certain mandatory fields details below.
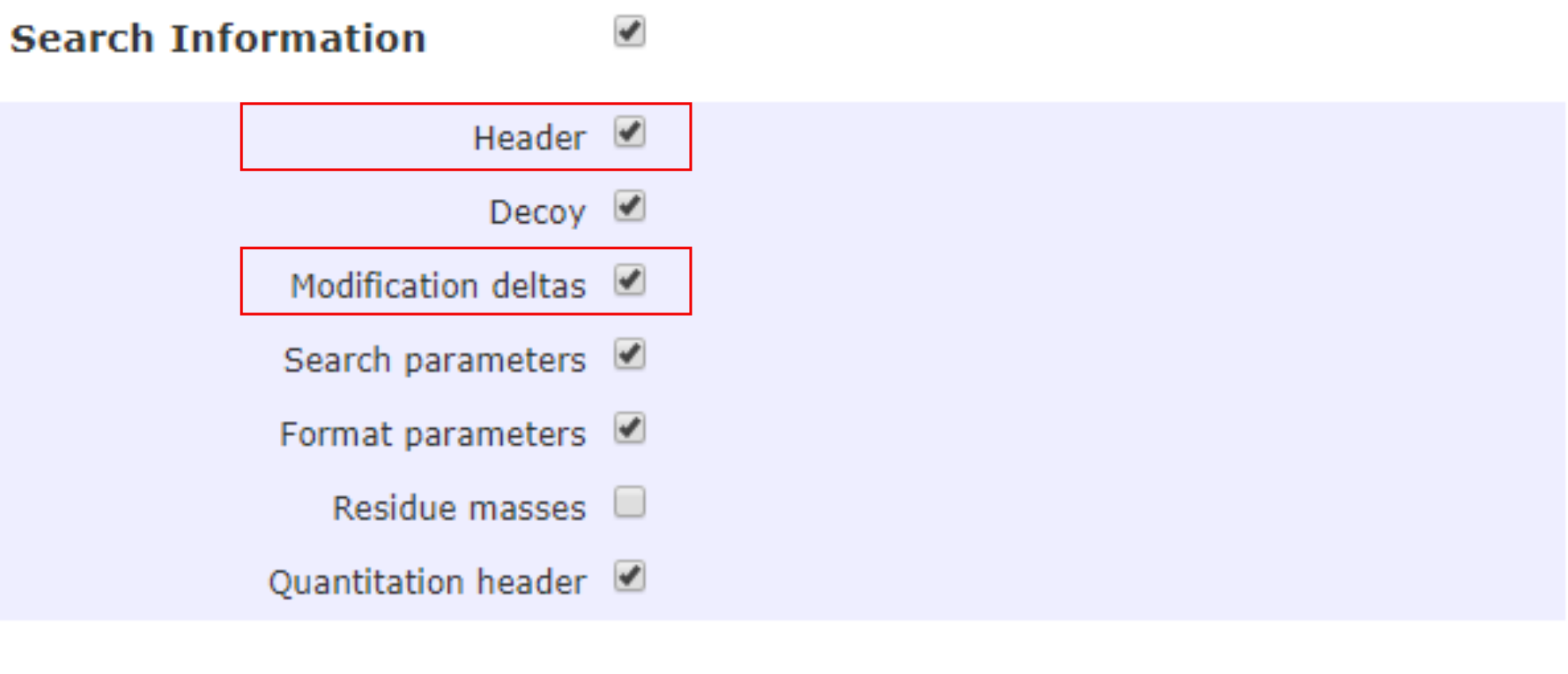
Search information
Under Search Information, the options of Header and Modification deltas should be checked to include information such as database(s), and assumptions in the fixed and variable modifications of amino acid residues.
Protein and pepide information
Under Protein hit information, we may also enable as many items as possible. Note that values from (1) Percent coverage would be reassessed (following the merge of one to multiple pieces of PSM data) and (2) Protein Quantitation be detached for downstream procedures. Thus, we might simply uncheck these options to save us some time.
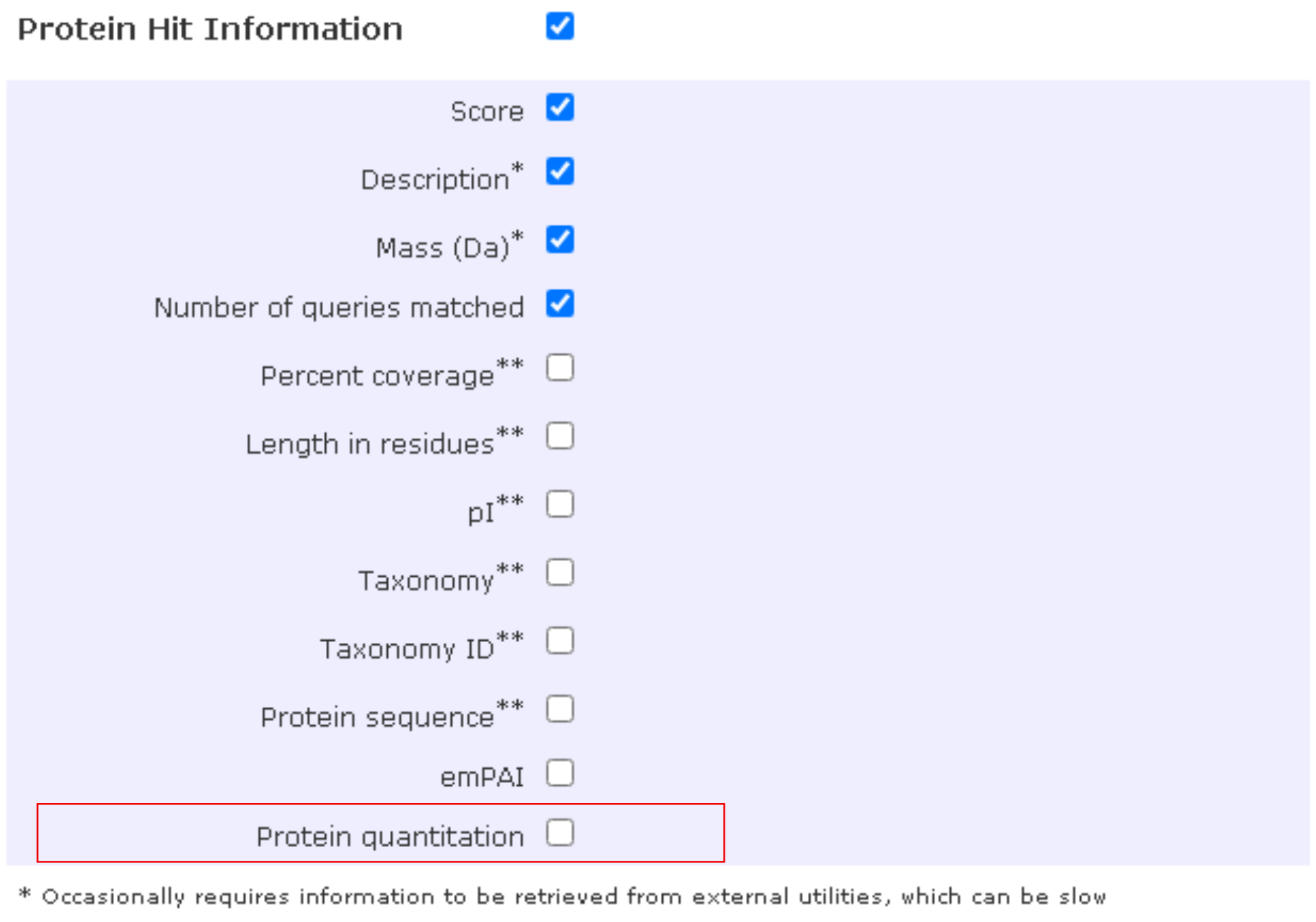
Under Peptide Match Information, the boxes linked to Sequence, Variable Modifications and Query title need to be ticked to enable the column keys of pep_seq, pep_var_mod_pos and pep_scan_title, respectively, in PSM outputs. The Peptide quantitation is also required with TMT workflows, to include reporter-ion intensities.

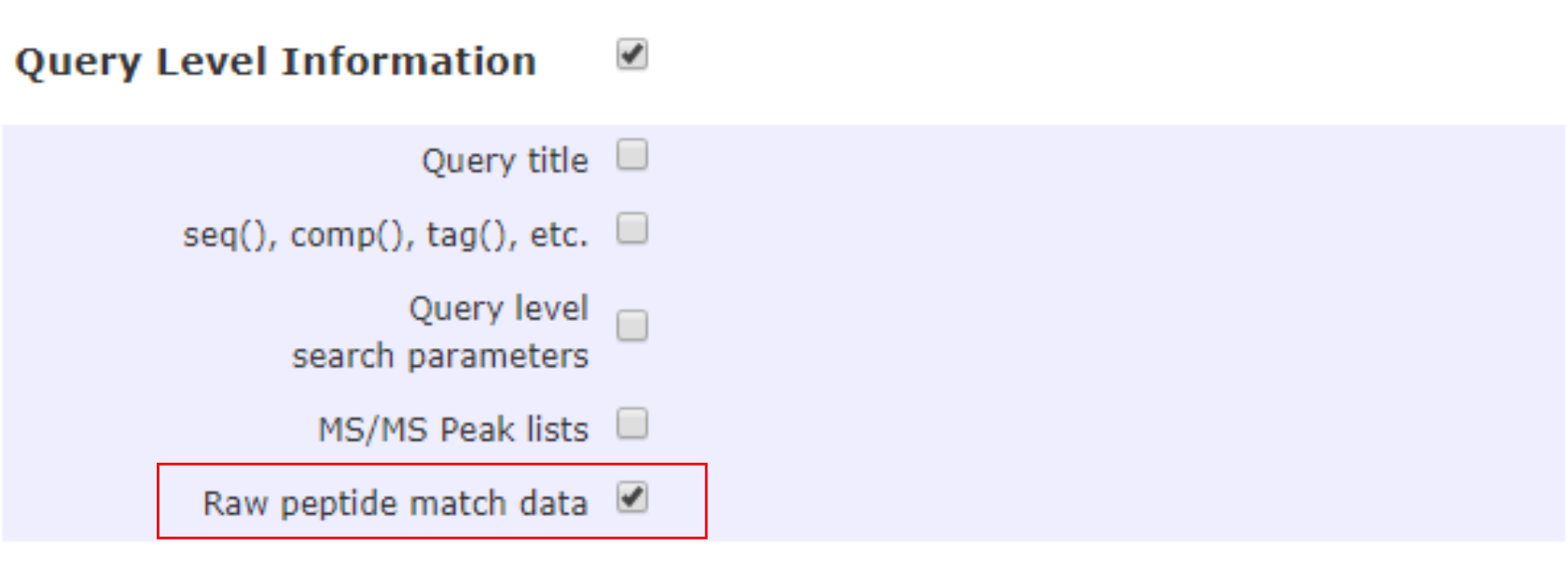
Query level information
More data may be incorporated into proteoQ reports by checking the Raw peptide match data under Query level information. This would bring information such as the intensity of precursor ions and the probability in the localization of peptide variable modifications, etc. Note that MS/MS Peak lists would enable the lists of MS/MS ions in a query, which might however take considerably more time to process.
Merged search
The same peptide sequence under different PSM files may be assigned to different protein IDs when inferring proteins from peptides using algorithms such as greedy set cover. To escape from the ambiguity in protein inference, I typically enable the option of Merge MS/MS files into single search in Mascot Daemon.2 If the option is disabled, peptide sequences that have been assigned to multiple protein IDs will be simply ascribed to the protein with the greatest number of identifying peptides, when possible.
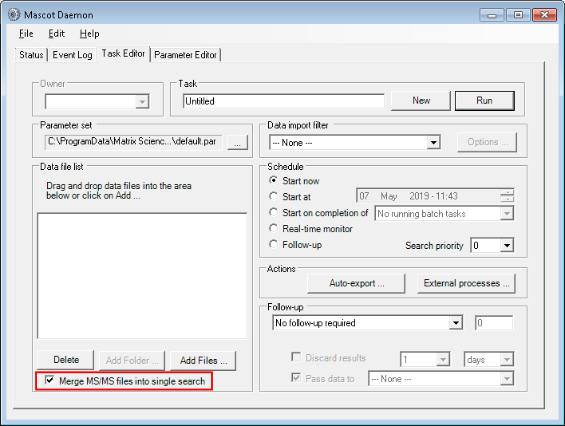
The merged search may become increasingly cumbersome with growing data sets. In the examples of TMT shown in proteoQ, I combined the MS peak lists from the pre-LCMS, Hp-RP fractions within the same 10-plex TMT experiment, but not the lists across experiments.
More precisely, they will be collapsed into the character strings under columns
shared_prot_accsandshared_genesin proteoQ outputs.↩︎There are cases that the same peptide sequence being assigned to different proteins remain unambiguous. For example, peptide
MENGQSTAAKcan be found from either the middle region of proteinNP_510965or the N-terminal of proteinNP_001129505. In case of the additional information of protein, not peptide, N-terminal acetylation, the sequence can only come fromNP_001129505between the two candidate proteins. In addition to handling such exceptions, the nomenclature inproteoQwill annotate the former asMENGQSTAAKand the later as_MENGQSTAAK.↩︎